Contemporaneous Notes on Elements and Technology = "ELT/TECH"
Contemporaneous Developments in Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry = "Org/Bio"
GENERAL/ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY
DECADE
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
1791: GALVANI discovers "animal electricity."
( VOLTA )
VOLTA )
1792-4: J. RICHTER: "ANFANGSGRUNDEN DER STOICHIOMETRIE." ("Basics of Stoichiometry") Determines constant combining proportions and "equivalents," especially of acids and alkalies.
1790
Return to top
ELT/TECH
-
1800: VOLTA shows that "animal electricity" is not of animal origin but from contact of metals. Produces "current electricity." Is this due to chemical action or to mere contact of metals?
(  Voltaic Pile )
Voltaic Pile )
1800: The Voltaic Pile. NICHOLSON and CARLISLE produce hydrogen and oxygen by electrolysis of water.
 1803-1807: BERZELIUS and HISINGER. Decomposition of salts by electrolysis.
1803-1807: BERZELIUS and HISINGER. Decomposition of salts by electrolysis.
DAVY identifies electricity with chemical affinity ;
(  BERZELIUS' DUALISTIC THEORY. )
BERZELIUS' DUALISTIC THEORY. )
 1805: GROTTHUSS' theory of electrolysis.
1805: GROTTHUSS' theory of electrolysis.
 DAVY isolates the alkali metals by electrolysis, supposing them at first to be hydrogen compounds; establishes (1810) the elementary nature of chlorine.
DAVY isolates the alkali metals by electrolysis, supposing them at first to be hydrogen compounds; establishes (1810) the elementary nature of chlorine.
 Controversy between PROUST and BERTHOLLET over the
Controversy between PROUST and BERTHOLLET over the
Law of Constant Proportions. PROUST finally establishes its truth.
{ WOLLASTON confirms experimentally the Law of Multiple Proportions, determining many "equivalent weights." > BERZELIUS and combining weights.
1808: GAY-LUSSAC'S Law of Combining Volumes. Gases combine in volume proportions of whole numbers. } 
 AVOGADRO'S HYPOTHESIS.
AVOGADRO'S HYPOTHESIS.
 DALTON proposes THE ATOMIC THEORY (Announced in T. THOMSON'S "SYSTEM OF CHEMISTRY" (1807) and in DALTON'S "NEW SYSTEM OF CHEMICAL PHILOSOPHY" (1808):
DALTON proposes THE ATOMIC THEORY (Announced in T. THOMSON'S "SYSTEM OF CHEMISTRY" (1807) and in DALTON'S "NEW SYSTEM OF CHEMICAL PHILOSOPHY" (1808):
1. Every element consists of homogeneous atoms, all of which have the same constant weight.
2. Compounds are formed by union of atoms of different elements in simple proportions.
Leads to PROUT'S Hypothesis.
1800
Return to top
ELT/TECH
Org/Bio
1803: BERTHOLLET: "ESSAE DE STATIQUE CHIMIQUE"
HENRY'S Law.
1811: AVOGADRO'S HYPOTHESIS:
Equal volumes of gases contain equal numbers of "molecules." The physical atom (molecule) of an elementary gas is not the same as a chemical atom. The former may consist of several of the latter. Same principle announced independently by AMPÉRE in 1814.
 THE VOLUME THEORY OF ATOMS (see below)
THE VOLUME THEORY OF ATOMS (see below)
Connections of Avogadro to DUMAS, FARADAY and LAURENT and GERHARDT.
PROUT'S Hypothesis: Atomic Weights are multiples of hydrogen.
Connected to Dalton's (prior) atomic theory.
DALTON unsuccessful in determining atomic weights. Used arbitrary symbols for atoms (Greek letters, circled "+", etc.); modern system of symbols and notation was introduced by BERZELIUS later in this decade.
DALTON rejects the idea that gas densities are proportional to atomic weights.
Many doubt the possibility of determining which multiples represent the true atomic weights.
 Possiblity of solving this problem suggested by DULONG and PETIT'S Law of Atomic Heats (1819) and MITSCHERLICH'S Law of Isomorphism.
Possiblity of solving this problem suggested by DULONG and PETIT'S Law of Atomic Heats (1819) and MITSCHERLICH'S Law of Isomorphism.
 Laurent and Gerhardt's atomic weights.(~1845)
Laurent and Gerhardt's atomic weights.(~1845)
BERZELIUS makes many careful determinations of combining weights, confirming WOLLASTON'S Law of Multiple Proportions.
 THE VOLUME THEORY OF ATOMS
THE VOLUME THEORY OF ATOMS
BERZELIUS' DUALISTIC THEORY: All compounds, organic and inorganic, consist of a positive and a negative part. Elements are either electropositive or electronegative. BERZELIUS' ideas lead to DUMAS' Etherin Theory and THE RADICAL THEORY.
Earlier in this decade, GAY-LUSSAC and THENARD on iodine and cyanogen (First compound "radical").
1810
Return to top
ELT/TECH
Org/Bio
(1818: GROTTHUSS' Photochemical Absorption Law
(leads to work by DRAPER and BUNSEN.)
BERZELIUS' greatest work was in the substantiation of the Atomic Theory.
He determined many atomic weights by study of composition, reactions, by analogy, etc.
DUMAS' method for vapor density determination. Unsuccessful in fixing atomic weights.
DÖBEREINER'S Triads.
(Developed from Prout's hypothesis and Dalton's Atomic Theory.)
1820
Return to top
ELT/TECH
Org/Bio
1823: FARADAY and DAVY on liquefaction of gases.
1824: CARNOT: Second law of thermodynamics.
"Brownian movement" observed.
GRAHAM discovers polybasic nature of phosphoric acid
and the relation of water and nonmetal oxide in acids.
 LIEBIG and WÖHLER extend Graham's observations of polybasic acids
LIEBIG and WÖHLER extend Graham's observations of polybasic acids
to the polybasic organic acids.
 Downfall of Oxygen Theory of Acids.
Downfall of Oxygen Theory of Acids.
1834: FARADAY'S Law. Electrochemical equivalent.
 idea of "valence" (1852)
idea of "valence" (1852)
1830
Return to top
ELT/TECH
Org/Bio
GRAHAM on diffusion of gases.
"Adsorption" of hydrogen by platinum---- FARADAY
DOWNFALL OF OXYGEN THEORY OF ACIDS
(as espoused earlier by LAVOISIER).
New concept: An acid contains hydrogen which can be replaced by a metal.
STAS' accurate work on atomic weights, extending over many years, establishes the exactness of laws of chemical combination and of conservation of mass.
1843: DUMAS: Combining proportions of hydrogen and oxygen.
LAURENT and GERHARDT define atomic weights in terms of twice the volume of the unit weight of hydrogen. Distinguish among atom, molecule and equivalent.
1840
Return to top
ELT/TECH
Org/Bio
DRAPER'S photochemical work based on that of GROTTHUSS (1818). Leads to work by BUNSEN and ROSCOE.
1840: Law of HESS. Beginning of thermochemistry.
1849: GRAHAM on diffusion of liquids.
1849: FRANKLAND: Metal alkyls.
 idea of
idea of "valence" (1852)
1851: WILLIAMSON: "ON THE CONSTITUTION OF SALTS." Substitution of atoms. Distinguishes between atom and molecule of an element.
{ 1852: First idea of VALENCE (or "Saturation Capacity"), based on observations of Faraday (1834) and Frankland (1849). Further discussion. }
 1855: ODLING: Atoms have "replacement" or substitution values.
1855: ODLING: Atoms have "replacement" or substitution values.  KEKULÉ (quadrivalence of carbon and formation of carbon chains, 1858)
KEKULÉ (quadrivalence of carbon and formation of carbon chains, 1858)
Graphic formulas----KEKULÉ and COUPER
 MODERN CONCEPTION OF
MODERN CONCEPTION OF
VALENCE AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
 Kekulé's benzene ring.
Kekulé's benzene ring.
GERHARDT (~1855): Formulas can only express reactions and relations of compounds. Atomic arrangement is impossible to determine.
1850
Return to top
ELT/TECH
Org/Bio
1852: BUNSEN and ROSCOE'S photochemical work. (based on DRAPER'S 1840 work.)
BUNSEN and G. R. KIRCHHOFF: Spectroscopic analysis.  identification of rubidium and cesium and helium.
identification of rubidium and cesium and helium.
HITTORF: Migration of ions and transference numbers.
KINETIC THEORY OF GASES developed by
- KRÖNIG (1856)
- CLAUSIUS (1857)
- G. R. KIRCHHOFF (1857)
DEVILLE: high temperature reactions
(e.g., decomposition of water)
 effects on equilibria.
effects on equilibria.
CLAUSIUS: Equilibrium of ions and molecules. (  Arrhenius' Theory of Electrolytic Dissociation (~1888).
Arrhenius' Theory of Electrolytic Dissociation (~1888).
1860: Karlsruhe meeting. CANNIZZARO explains how to fix values for atomic weights. (based upon previous work of Avogadro, Döbereiner and Laurent and Gerhardt)

MODERN CONCEPTION OF VALENCE AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
1861: GRAHAM: Dialysis and distinction between colloids and crystalloids. (based upon earlier work by Graham (1849).
 DE CHANCOURTOIS
DE CHANCOURTOIS
 NEWLANDS' (1865) Law of Octaves
NEWLANDS' (1865) Law of Octaves >
1869: THE PERIODIC LAW:
MENDELEEV and L MEYER
Vicinity of the "Periodic Law" in the "Mallinckrodt Outline of the History of Chemistry".
1860
Return to top
ELT/TECH
Org/Bio
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
1863: GULDBERG and WAAGE: Law of Mass Action (based in part on by Berthelot and De St. Gilles.)
( VAN'T HOFF(1884) on equilibrium and Ostwald Dilution Law.
VAN'T HOFF(1884) on equilibrium and Ostwald Dilution Law.
1869: GOLDSTEIN: Discovery of cathode rays.
1869: BERTHELOT'S thermochemical studies.
( 1879 Law of Maximum Work)
1879 Law of Maximum Work)
1874: VAN'T HOFF and LE BEL: independently establish the foundations of STEREOCHEMISTRY based in part upon work of Pasteur.
CROOKES' Cathode rays are negatively charged particles.
 Stoney, et al.
Stoney, et al.
1870
Return to top
ELT/TECH
Org/Bio
ANDREWS: Conception of critical temperature and pressure.
The CLARK standard cell.
1873: VAN DER WAALS'S equation.
1876: KOHLRAUSCH: relative migration velocities (based on work of Hittorf and Clausius.
GIBBS' Phase Rule. Chemical thermodynamics.
1877: PFEFFER'S measurements of osmotic pressure.
( Raoult)
Raoult)
1878: VICTOR MEYER'S work on vapor densities. Dissociation of iodine.
1879: Law of Maximum Work
1886: GOLDSTEIN: Discovery of "canal rays."
1887:WISLICENUS: "DIE LAGERUNG DER ATOME IM RAUME"
("THE ARRANGEMENT OF ATOMS IN SPACE")
1888: LE CHATELIER'S Principle.
1880
Return to top
ELT/TECH
HELMHOLTZ applies thermodynamics to electrochemistry.
1881: RAOULT: Freezing and Boiling Point Laws.
 VAN'T HOFF applies gas laws to solutions.
VAN'T HOFF applies gas laws to solutions.
( Arrhenius)
Arrhenius)
1882: THOMSEN thermochemical studies.
1884: VAN'T HOFF on equilibrium.
1885: OSTWALD Dilution Law.
NERNST'S osmotic theory of electrochemical action.
THEORY OF ELECTROLYTIC DISSOCIATION
---- ARRHENIUS ( Sutherland)
Sutherland)
Vicinity of the "Theory of Electrolytic Dissociation" in the "Mallinckrodt Outline of the History of Chemistry".
1889: NERNST: Concept of Solubility Product.
1891: Term "electron" ---- STONEY.
1892: WERNER: The metal ammonia complexes.
Inorganic stereoisomerism. Co-ordination numbers.
OSTWALD: theory of indicators. (  HANTZSCH )
HANTZSCH )
1895: Completion of MORLEY'S work on the combining ratio
of oxygen and hydrogen.
1895: RÖNTGEN: X-rays.
1896: WILSON: First cloud chamber.
1896: BECQUEREL: Radioactivity of uranium.
1897: WIECHART and J. J. THOMSON: "Radiant matter" ----
negative corpuscles from breakdown of atoms
( Thomson atom and
Thomson atom and
Electron theory of valence.)
( Bohr atom)
Bohr atom)
Vicinity of the Bohr atom, etc., in the "Mallinckrodt Outline of the History of Chemistry".
1899: E. RUTHERFORD: α and β rays.
1899: THIELE'S partial valence theory.
1890
Return to top
ELT/TECH
Org/Bio
The WESTON standard cell.
Tautomeric theory of indicators (HANTZSCH, based on Ostwald's work)
Liquifaction of hydrogen  Onnes
Onnes
{ 1900: BECQUEREL: β rays = cathode rays. VILLARD: Discovery of α rays.
1902: E. RUTHERFORD and SODDY: Radioactivity and atomic disintegration.
1903: RAMSAY and SODDY: Helium from uranium. }
 The J. J. THOMSON atom.
The J. J. THOMSON atom.
 Electronic theory of valence. (
Electronic theory of valence. ( Debye)
Debye)
 nuclear atom.
nuclear atom.
1903: RICHARDS and pupils on revision of atomic weight values.
1904: KIPPING: investigation of silanes, which was basis
for later development of silicone industry.
1905: EINSTEIN: Photoelectrical theory. Special theory of relativity.
MASS-ENERGY EQUIVALENCE. E = mc2
1909: E. RUTHERFORD: α rays are helium (ions).
1900
Return to top
ELT/TECH
Org/Bio
1900: PLANCK: The Quantum Theory.
SUTHERLAND: Theory of complete ionization.
BJERRUM.  Debye and Hückel.
Debye and Hückel.
1906: NERNST: Heat Theorem. Third Law of Thermodynamics.
1907: LEWIS introduces the concept of "activity."
1907: MORSE and FRAZER'S measurements of osmotic pressure.
Use of "pH" --- SØRENSEN
ONNES: Liquifaction of Helium.
1911: E. RUTHERFORD: Discovery of nuclear atom.
 Bohr atom.
Bohr atom.
Vicinity of the Bohr atom in the "Mallinckrodt Outline of the History of Chemistry".
EINSTEIN: Law of Photochemical Equivalence.
"Active" nitrogen ----- STRUTT.
J. J. THOMSON: Positive Rays. "Meta-neon."
 Moseley and Aston.
Moseley and Aston.
1911: WILSON: Expansion cloud chamber---ionization tract.
 Aston.
Aston.
1913:BOHR ATOM. Theory of stationary states.
 SOMMERFELD: Quantum Numbers.
SOMMERFELD: Quantum Numbers.
ATOMIC NUMBERS ---- MOSELEY
 Aston.
Aston.
Scroll down to 1910 to view the vicinity of Atomic Numbers in the "Mallinckrodt Outline of the History of Chemistry".
1913: SODDY, FAJANS, RUSSELL: Group displacement law.
1913: SODDY: Isotope concept.
"LAUE'S Spots."
BRAGG and BRAGG: Crystal structure.
 Moseley
Moseley
1914: RICHARDS and LEMBERT: "Isotopic lead."
1915: BRAGG Fourier series. ( Robertson)
Robertson)
{1916: LEWIS and 1919: LANGMUIR} Theory of Atomic Structure  Electronic formulas
Electronic formulas
 Lewis' electronic theory of acids and bases.
Lewis' electronic theory of acids and bases.
1917: LANGMUIR: unimolecular film.
1919: E. RUTHERFORD: Artificial transmutation. Atom Nucleus. α particle bombardment of light elements.  GAMOW
GAMOW  Cockcroft.
Cockcroft.
1910
Return to top
ELT/TECH
Org/Bio
1911: DONNAN: Law of Membrane Equilibrium.
1912: DEBYE: theory of dipole moments. Polar and non-polar compounds.
RICHARDS: Compressibility of atoms.
1916: FREUNDLICH and LANGMUIR: Adsorption isotherm. ( Willstätter)
Willstätter)
1919: ASTON: Mass Spectrograph. Isotopic elements. Whole Number Rule.
1920: KRATZER--- Molecular spectra.
 CZERNY --- rotation, vibration
CZERNY --- rotation, vibration
 infrared spectroscopy
infrared spectroscopy  Structure.
Structure.
1923: SMEKAL--- light scatter frequency characteristic of liquids.
 SMEKAL-RAMAN effect.
SMEKAL-RAMAN effect.
 Structure
Structure
MILLIKAN: Cosmic rays.
COMPTON effect.
BRØNSTED and HEVESY: mercury isotopes.
HARKINS et al.: chlorine isotopes.
( HEVESY ---- 212Pb )
HEVESY ---- 212Pb )
E. RUTHERFORD
 { HARKINS element "neutron"
{ HARKINS element "neutron"
 CHADWICK (discovery of the neutron) }
CHADWICK (discovery of the neutron) }
 beta ray emission
beta ray emission  Pauli.
Pauli.
1923: BRØNSTED theory.  LEWIS (Electronic theory of acids and bases) and SIDGWICK (Covalency Rule)
LEWIS (Electronic theory of acids and bases) and SIDGWICK (Covalency Rule)
 Pauling.
Pauling.
1925: HEYROVSKÝ: Polarography.
G. P. THOMSON et al.: crystal analysis ( elucidation of Structure. Related work by LONSDALE
elucidation of Structure. Related work by LONSDALE
1920
Return to top
ELT/TECH
Org/Bio
LEWIS and RANDALL--- ionic activity (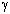 , c)
, c)
1923: DE BROGLIE: electron diffraction.
DEBYE and HÜCKEL
 DEBYE-HÜCKEL-ONSAGER Equation.
DEBYE-HÜCKEL-ONSAGER Equation.
PAULI: Neutrino Hypothesis
 FERMI: β-Decay Theory
FERMI: β-Decay Theory
 neutrino (1950's)
neutrino (1950's)
DIRAC > C. D. ANDERSON: Positron.
PAULING--- Resonance
--(culmination of previous spectroscopy, x-ray and electron diffraction, crystal analysis and bonding theories by Lewis, et al.), and HOUWINK'S study of physical properties and structure.
 STRUCTURE.
STRUCTURE.
1933: ROBERTSON: X-ray analysis structure.
1933: RABI
 1935: BORN: Optical rotary power
1935: BORN: Optical rotary power
 Chemical bond and atom orientation.
Chemical bond and atom orientation.
( infrared spectroscopy, in 1940's).
infrared spectroscopy, in 1940's).
JOLIOT-CURIE: Artificial Radioactivity
 1934: FERMI: neutron bombardment.
1934: FERMI: neutron bombardment.
 FERMI: "Transuranium elements"
FERMI: "Transuranium elements"
 Thermal neutrons.
Thermal neutrons.
 HAHN and STRASSMANN
HAHN and STRASSMANN
 MEITNER and FRISCH
MEITNER and FRISCH
 Nuclear Fission.
Nuclear Fission.
1930
Return to top
ELT/TECH
Org/Bio
YUKAWA Prediction of Meson.
Cosmic rays  C. D. ANDERSON: Meson.
C. D. ANDERSON: Meson.
 light meson
light meson
PAULI Neutrino Hypothesis.
 FERMI β-Decay Theory.
FERMI β-Decay Theory.
COCKCROFT and WALTON:
- Nuclear transmutation.
- Artif. accel. particles.
 PARTICLE ACCELERATORS
PARTICLE ACCELERATORS
 LAWRENCE----Cyclotron.
LAWRENCE----Cyclotron.
 Electrostatic Generators
Electrostatic Generators
 Betatron
Betatron  (1940's) Linear Accelerators
(1940's) Linear Accelerators
NUCLEAR FISSION  SPALLATION
SPALLATION
> FERMI: ATOMIC PILE
(first self-maintaining Nuclear Chain Reaction)
 (given U235 and Pu239) ATOMIC BOMB and NUCLEAR REACTORS in which regeneration of fuel can occur .
(given U235 and Pu239) ATOMIC BOMB and NUCLEAR REACTORS in which regeneration of fuel can occur .
ATOMIC BOMB  Nuclear Fusion (see below)
Nuclear Fusion (see below)
ION EXCHANGE: applied to separation of radioisotopes.
Linear Accelerators > Synchrotron Principle > Electron Synchrotron  Synchro-Cyclotron
Synchro-Cyclotron  (1950's)Cosmotron
(1950's)Cosmotron
Infrared spectroscopy and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
 ORGANIC SYNTHESIS
ORGANIC SYNTHESIS
- Quinine
- Morphine
- Oxytocin
- Strychnine
- Cortisone
- Biotin, etc.
Electron Paramagnetic Resonance
Molecular Orbital Theory
1940
Return to top
ELT/TECH
Org/Bio
NONEQUILIBRIUM THERMODYNAMICS (PRIGOGINE)
Light Mesons
 heavy mesons
heavy mesons
 Hyperons(1950's)
Hyperons(1950's)
LIBBY: C14 DATING
 tritium dating
tritium dating
NUCLEAR FUSION (H2 and H3) --- HYDROGEN BOMB
Carbon cycle and proton-proton chain
 Pinch Effect
Pinch Effect
 Eventual expected utilization of fusion energy
Eventual expected utilization of fusion energy
Geochemistry and Magnetochemistry
Complexes and Crystal Field Theory
Neutrino and antineutrino (based upon Fermi's Beta-Decay Theory)  Parity Laws (mentioned at right
Parity Laws (mentioned at right  )
)
Cosmotron  Bevatron
Bevatron
 (~1960) Alternating Gradient Synchrotron
(~1960) Alternating Gradient Synchrotron
1950
Return to top
ELT/TECH
Org/Bio
Hyperons (and neutrino/antineutrino)
 LEE and YANG: Parity laws.
LEE and YANG: Parity laws.
1962: BARTLETT: first noble gas (xenon) compounds
1960
Return to top
ELT/TECH
Org/Bio
Beginnings of Computational Chemistry
-
1970
Return to top
ELT/TECH
Org/Bio
-
1985 - KROTO and WALTON: C60 (fullerene)
1988 - Scanning Tunnelling Microscope images a benzene molecule
1980
Return to top
ELT/TECH
Org/Bio
-
-
1990
Return to top
ELT/TECH
Org/Bio
-
GENERAL/ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY |
DECADE |
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY |
1791: GALVANI discovers "animal electricity."  VOLTA ) VOLTA )1792-4: J. RICHTER: "ANFANGSGRUNDEN DER STOICHIOMETRIE." ("Basics of Stoichiometry") Determines constant combining proportions and "equivalents," especially of acids and alkalies. |
1790Return to top ELT/TECH |
- |
1800: VOLTA shows that "animal electricity" is not of animal origin but from contact of metals. Produces "current electricity." Is this due to chemical action or to mere contact of metals?  Voltaic Pile ) Voltaic Pile )1800: The Voltaic Pile. NICHOLSON and CARLISLE produce hydrogen and oxygen by electrolysis of water.  1803-1807: BERZELIUS and HISINGER. Decomposition of salts by electrolysis. 1803-1807: BERZELIUS and HISINGER. Decomposition of salts by electrolysis.  BERZELIUS' DUALISTIC THEORY. ) BERZELIUS' DUALISTIC THEORY. ) 1805: GROTTHUSS' theory of electrolysis. 1805: GROTTHUSS' theory of electrolysis. DAVY isolates the alkali metals by electrolysis, supposing them at first to be hydrogen compounds; establishes (1810) the elementary nature of chlorine. DAVY isolates the alkali metals by electrolysis, supposing them at first to be hydrogen compounds; establishes (1810) the elementary nature of chlorine.  Controversy between PROUST and BERTHOLLET over the Controversy between PROUST and BERTHOLLET over the  AVOGADRO'S HYPOTHESIS. AVOGADRO'S HYPOTHESIS. DALTON proposes THE ATOMIC THEORY (Announced in T. THOMSON'S "SYSTEM OF CHEMISTRY" (1807) and in DALTON'S "NEW SYSTEM OF CHEMICAL PHILOSOPHY" (1808): DALTON proposes THE ATOMIC THEORY (Announced in T. THOMSON'S "SYSTEM OF CHEMISTRY" (1807) and in DALTON'S "NEW SYSTEM OF CHEMICAL PHILOSOPHY" (1808):
1. Every element consists of homogeneous atoms, all of which have the same constant weight. |
1800Return to top ELT/TECH Org/Bio |
1803: BERTHOLLET: "ESSAE DE STATIQUE CHIMIQUE" HENRY'S Law. |
1811: AVOGADRO'S HYPOTHESIS:
Equal volumes of gases contain equal numbers of "molecules." The physical atom (molecule) of an elementary gas is not the same as a chemical atom. The former may consist of several of the latter. Same principle announced independently by AMPÉRE in 1814.  THE VOLUME THEORY OF ATOMS (see below) THE VOLUME THEORY OF ATOMS (see below)PROUT'S Hypothesis: Atomic Weights are multiples of hydrogen. DALTON unsuccessful in determining atomic weights. Used arbitrary symbols for atoms (Greek letters, circled "+", etc.); modern system of symbols and notation was introduced by BERZELIUS later in this decade.  Possiblity of solving this problem suggested by DULONG and PETIT'S Law of Atomic Heats (1819) and MITSCHERLICH'S Law of Isomorphism. Possiblity of solving this problem suggested by DULONG and PETIT'S Law of Atomic Heats (1819) and MITSCHERLICH'S Law of Isomorphism.  Laurent and Gerhardt's atomic weights.(~1845) Laurent and Gerhardt's atomic weights.(~1845)BERZELIUS makes many careful determinations of combining weights, confirming WOLLASTON'S Law of Multiple Proportions.  THE VOLUME THEORY OF ATOMS THE VOLUME THEORY OF ATOMSBERZELIUS' DUALISTIC THEORY: All compounds, organic and inorganic, consist of a positive and a negative part. Elements are either electropositive or electronegative. BERZELIUS' ideas lead to DUMAS' Etherin Theory and THE RADICAL THEORY. Earlier in this decade, GAY-LUSSAC and THENARD on iodine and cyanogen (First compound "radical"). |
1810Return to top ELT/TECH Org/Bio |
(1818: GROTTHUSS' Photochemical Absorption Law |
| BERZELIUS' greatest work was in the substantiation of the Atomic Theory. He determined many atomic weights by study of composition, reactions, by analogy, etc. DUMAS' method for vapor density determination. Unsuccessful in fixing atomic weights. DÖBEREINER'S Triads. |
1820Return to top ELT/TECH Org/Bio |
1823: FARADAY and DAVY on liquefaction of gases. 1824: CARNOT: Second law of thermodynamics. "Brownian movement" observed. |
GRAHAM discovers polybasic nature of phosphoric acid  LIEBIG and WÖHLER extend Graham's observations of polybasic acids LIEBIG and WÖHLER extend Graham's observations of polybasic acids  Downfall of Oxygen Theory of Acids. Downfall of Oxygen Theory of Acids. 1834: FARADAY'S Law. Electrochemical equivalent.  idea of "valence" (1852) idea of "valence" (1852)
|
1830Return to top ELT/TECH Org/Bio |
GRAHAM on diffusion of gases. "Adsorption" of hydrogen by platinum---- FARADAY |
|
DOWNFALL OF OXYGEN THEORY OF ACIDS STAS' accurate work on atomic weights, extending over many years, establishes the exactness of laws of chemical combination and of conservation of mass. 1843: DUMAS: Combining proportions of hydrogen and oxygen. LAURENT and GERHARDT define atomic weights in terms of twice the volume of the unit weight of hydrogen. Distinguish among atom, molecule and equivalent. |
1840Return to top ELT/TECH Org/Bio |
DRAPER'S photochemical work based on that of GROTTHUSS (1818). Leads to work by BUNSEN and ROSCOE. 1840: Law of HESS. Beginning of thermochemistry. 1849: GRAHAM on diffusion of liquids. 1849: FRANKLAND: Metal alkyls.  idea of idea of |
1851: WILLIAMSON: "ON THE CONSTITUTION OF SALTS." Substitution of atoms. Distinguishes between atom and molecule of an element. 1855: ODLING: Atoms have "replacement" or substitution values. 1855: ODLING: Atoms have "replacement" or substitution values.  KEKULÉ (quadrivalence of carbon and formation of carbon chains, 1858) KEKULÉ (quadrivalence of carbon and formation of carbon chains, 1858)Graphic formulas----KEKULÉ and COUPER  MODERN CONCEPTION OF MODERN CONCEPTION OF  Kekulé's benzene ring. Kekulé's benzene ring.GERHARDT (~1855): Formulas can only express reactions and relations of compounds. Atomic arrangement is impossible to determine. |
1850Return to top ELT/TECH Org/Bio |
1852: BUNSEN and ROSCOE'S photochemical work. (based on DRAPER'S 1840 work.) BUNSEN and G. R. KIRCHHOFF: Spectroscopic analysis.  identification of rubidium and cesium and helium. identification of rubidium and cesium and helium.HITTORF: Migration of ions and transference numbers. KINETIC THEORY OF GASES developed by
 effects on equilibria. effects on equilibria.CLAUSIUS: Equilibrium of ions and molecules. (  Arrhenius' Theory of Electrolytic Dissociation (~1888). Arrhenius' Theory of Electrolytic Dissociation (~1888).
|
1860: Karlsruhe meeting. CANNIZZARO explains how to fix values for atomic weights. (based upon previous work of Avogadro, Döbereiner and Laurent and Gerhardt) MODERN CONCEPTION OF VALENCE AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE1861: GRAHAM: Dialysis and distinction between colloids and crystalloids. (based upon earlier work by Graham (1849).  DE CHANCOURTOIS DE CHANCOURTOIS  NEWLANDS' (1865) Law of Octaves NEWLANDS' (1865) Law of Octaves 1869: THE PERIODIC LAW:
Vicinity of the "Periodic Law" in the "Mallinckrodt Outline of the History of Chemistry". |
1860Return to top ELT/TECH Org/Bio |
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY1863: GULDBERG and WAAGE: Law of Mass Action (based in part on by Berthelot and De St. Gilles.)  VAN'T HOFF(1884) on equilibrium and Ostwald Dilution Law. VAN'T HOFF(1884) on equilibrium and Ostwald Dilution Law.1869: GOLDSTEIN: Discovery of cathode rays. 1869: BERTHELOT'S thermochemical studies.  1879 Law of Maximum Work) 1879 Law of Maximum Work)
|
|
1874: VAN'T HOFF and LE BEL: independently establish the foundations of STEREOCHEMISTRY based in part upon work of Pasteur. CROOKES' Cathode rays are negatively charged particles.  Stoney, et al. Stoney, et al. |
1870Return to top ELT/TECH Org/Bio |
ANDREWS: Conception of critical temperature and pressure. The CLARK standard cell. 1873: VAN DER WAALS'S equation. 1876: KOHLRAUSCH: relative migration velocities (based on work of Hittorf and Clausius. GIBBS' Phase Rule. Chemical thermodynamics. 1877: PFEFFER'S measurements of osmotic pressure.  Raoult) Raoult) 1878: VICTOR MEYER'S work on vapor densities. Dissociation of iodine. 1879: Law of Maximum Work |
|
1886: GOLDSTEIN: Discovery of "canal rays." 1887:WISLICENUS: "DIE LAGERUNG DER ATOME IM RAUME" 1888: LE CHATELIER'S Principle. |
1880Return to top ELT/TECH |
HELMHOLTZ applies thermodynamics to electrochemistry. 1881: RAOULT: Freezing and Boiling Point Laws.  VAN'T HOFF applies gas laws to solutions. VAN'T HOFF applies gas laws to solutions. Arrhenius) Arrhenius)1882: THOMSEN thermochemical studies. 1884: VAN'T HOFF on equilibrium. 1885: OSTWALD Dilution Law. NERNST'S osmotic theory of electrochemical action. THEORY OF ELECTROLYTIC DISSOCIATION  Sutherland) Sutherland)Vicinity of the "Theory of Electrolytic Dissociation" in the "Mallinckrodt Outline of the History of Chemistry".1889: NERNST: Concept of Solubility Product. |
|
1891: Term "electron" ---- STONEY. 1892: WERNER: The metal ammonia complexes. OSTWALD: theory of indicators. (  HANTZSCH ) HANTZSCH )1895: Completion of MORLEY'S work on the combining ratio 1895: RÖNTGEN: X-rays. 1896: WILSON: First cloud chamber. 1896: BECQUEREL: Radioactivity of uranium. 1897: WIECHART and J. J. THOMSON: "Radiant matter" ----  Thomson atom and Thomson atom and  Bohr atom) Bohr atom)Vicinity of the Bohr atom, etc., in the "Mallinckrodt Outline of the History of Chemistry".1899: E. RUTHERFORD: α and β rays. 1899: THIELE'S partial valence theory. |
1890Return to top ELT/TECH Org/Bio |
The WESTON standard cell. |
|
Tautomeric theory of indicators (HANTZSCH, based on Ostwald's work) Liquifaction of hydrogen  Onnes Onnes{ 1900: BECQUEREL: β rays = cathode rays.  The J. J. THOMSON atom. The J. J. THOMSON atom. Electronic theory of valence. ( Electronic theory of valence. ( Debye) Debye)
 nuclear atom. nuclear atom.1903: RICHARDS and pupils on revision of atomic weight values. 1904: KIPPING: investigation of silanes, which was basis 1905: EINSTEIN: Photoelectrical theory. Special theory of relativity. 1909: E. RUTHERFORD: α rays are helium (ions). |
1900Return to top ELT/TECH Org/Bio |
1900: PLANCK: The Quantum Theory. SUTHERLAND: Theory of complete ionization. BJERRUM.  Debye and Hückel. Debye and Hückel.1906: NERNST: Heat Theorem. Third Law of Thermodynamics. 1907: LEWIS introduces the concept of "activity." 1907: MORSE and FRAZER'S measurements of osmotic pressure. Use of "pH" --- SØRENSEN |
|
ONNES: Liquifaction of Helium. 1911: E. RUTHERFORD: Discovery of nuclear atom.  Bohr atom. Bohr atom.Vicinity of the Bohr atom in the "Mallinckrodt Outline of the History of Chemistry".EINSTEIN: Law of Photochemical Equivalence. "Active" nitrogen ----- STRUTT. J. J. THOMSON: Positive Rays. "Meta-neon."  Moseley and Aston. Moseley and Aston.1911: WILSON: Expansion cloud chamber---ionization tract.  Aston. Aston.1913:BOHR ATOM. Theory of stationary states.  SOMMERFELD: Quantum Numbers. SOMMERFELD: Quantum Numbers.ATOMIC NUMBERS ---- MOSELEY  Aston. Aston.Scroll down to 1910 to view the vicinity of Atomic Numbers in the "Mallinckrodt Outline of the History of Chemistry".1913: SODDY, FAJANS, RUSSELL: Group displacement law. 1913: SODDY: Isotope concept. "LAUE'S Spots." BRAGG and BRAGG: Crystal structure.  Moseley Moseley1914: RICHARDS and LEMBERT: "Isotopic lead." 1915: BRAGG Fourier series. (  Robertson) Robertson){1916: LEWIS and 1919: LANGMUIR} Theory of Atomic Structure  Electronic formulas Electronic formulas Lewis' electronic theory of acids and bases. Lewis' electronic theory of acids and bases.1917: LANGMUIR: unimolecular film. 1919: E. RUTHERFORD: Artificial transmutation. Atom Nucleus. α particle bombardment of light elements.  GAMOW GAMOW  Cockcroft. Cockcroft. |
1910Return to top ELT/TECH Org/Bio |
1911: DONNAN: Law of Membrane Equilibrium. 1912: DEBYE: theory of dipole moments. Polar and non-polar compounds. RICHARDS: Compressibility of atoms. 1916: FREUNDLICH and LANGMUIR: Adsorption isotherm. (  Willstätter) Willstätter)1919: ASTON: Mass Spectrograph. Isotopic elements. Whole Number Rule. |
1920: KRATZER--- Molecular spectra. CZERNY --- rotation, vibration CZERNY --- rotation, vibration infrared spectroscopy infrared spectroscopy  Structure. Structure.1923: SMEKAL--- light scatter frequency characteristic of liquids.  SMEKAL-RAMAN effect. SMEKAL-RAMAN effect. Structure Structure MILLIKAN: Cosmic rays. COMPTON effect. BRØNSTED and HEVESY: mercury isotopes. HARKINS et al.: chlorine isotopes.  HEVESY ---- 212Pb ) HEVESY ---- 212Pb )E. RUTHERFORD  { HARKINS element "neutron" { HARKINS element "neutron"  CHADWICK (discovery of the neutron) } CHADWICK (discovery of the neutron) } beta ray emission beta ray emission  Pauli. Pauli.1923: BRØNSTED theory.  LEWIS (Electronic theory of acids and bases) and SIDGWICK (Covalency Rule) LEWIS (Electronic theory of acids and bases) and SIDGWICK (Covalency Rule) Pauling. Pauling.1925: HEYROVSKÝ: Polarography. G. P. THOMSON et al.: crystal analysis (  elucidation of Structure. Related work by LONSDALE elucidation of Structure. Related work by LONSDALE |
1920Return to top ELT/TECH Org/Bio |
LEWIS and RANDALL--- ionic activity (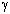 , c) , c)1923: DE BROGLIE: electron diffraction. DEBYE and HÜCKEL  DEBYE-HÜCKEL-ONSAGER Equation. DEBYE-HÜCKEL-ONSAGER Equation. |
PAULI: Neutrino Hypothesis FERMI: β-Decay Theory FERMI: β-Decay Theory neutrino (1950's) neutrino (1950's)DIRAC PAULING--- Resonance --(culmination of previous spectroscopy, x-ray and electron diffraction, crystal analysis and bonding theories by Lewis, et al.), and HOUWINK'S study of physical properties and structure.  STRUCTURE. STRUCTURE. 1933: ROBERTSON: X-ray analysis structure. 1933: RABI  1935: BORN: Optical rotary power 1935: BORN: Optical rotary power  Chemical bond and atom orientation. Chemical bond and atom orientation. infrared spectroscopy, in 1940's). infrared spectroscopy, in 1940's).JOLIOT-CURIE: Artificial Radioactivity  1934: FERMI: neutron bombardment. 1934: FERMI: neutron bombardment. FERMI: "Transuranium elements" FERMI: "Transuranium elements"  Thermal neutrons. Thermal neutrons. HAHN and STRASSMANN HAHN and STRASSMANN MEITNER and FRISCH MEITNER and FRISCH Nuclear Fission. Nuclear Fission. |
1930Return to top ELT/TECH Org/Bio |
YUKAWA Prediction of Meson. Cosmic rays  C. D. ANDERSON: Meson. C. D. ANDERSON: Meson. light meson light meson PAULI Neutrino Hypothesis.  FERMI β-Decay Theory. FERMI β-Decay Theory.COCKCROFT and WALTON:
 PARTICLE ACCELERATORS PARTICLE ACCELERATORS LAWRENCE----Cyclotron. LAWRENCE----Cyclotron. Electrostatic Generators Electrostatic Generators  Betatron Betatron  (1940's) Linear Accelerators (1940's) Linear Accelerators |
NUCLEAR FISSION  SPALLATION SPALLATION (given U235 and Pu239) ATOMIC BOMB and NUCLEAR REACTORS in which regeneration of fuel can occur . (given U235 and Pu239) ATOMIC BOMB and NUCLEAR REACTORS in which regeneration of fuel can occur . Nuclear Fusion (see below) Nuclear Fusion (see below)ION EXCHANGE: applied to separation of radioisotopes. Linear Accelerators  Synchro-Cyclotron Synchro-Cyclotron  (1950's)Cosmotron (1950's)CosmotronInfrared spectroscopy and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance  ORGANIC SYNTHESIS ORGANIC SYNTHESIS
Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Molecular Orbital Theory |
1940Return to top ELT/TECH Org/Bio |
NONEQUILIBRIUM THERMODYNAMICS (PRIGOGINE) Light Mesons  heavy mesons heavy mesons
 Hyperons(1950's) Hyperons(1950's) |
LIBBY: C14 DATING tritium dating tritium datingNUCLEAR FUSION (H2 and H3) --- HYDROGEN BOMB  Pinch Effect Pinch Effect Eventual expected utilization of fusion energy Eventual expected utilization of fusion energyGeochemistry and Magnetochemistry Complexes and Crystal Field Theory Neutrino and antineutrino (based upon Fermi's Beta-Decay Theory)  Parity Laws (mentioned at right Parity Laws (mentioned at right  ) )Cosmotron  Bevatron Bevatron (~1960) Alternating Gradient Synchrotron (~1960) Alternating Gradient Synchrotron
|
1950Return to top ELT/TECH Org/Bio |
Hyperons (and neutrino/antineutrino)  LEE and YANG: Parity laws. LEE and YANG: Parity laws.
|
| 1962: BARTLETT: first noble gas (xenon) compounds |
1960Return to top ELT/TECH Org/Bio |
Beginnings of Computational Chemistry |
| - |
1970Return to top ELT/TECH Org/Bio |
- |
|
1985 - KROTO and WALTON: C60 (fullerene) 1988 - Scanning Tunnelling Microscope images a benzene molecule |
1980Return to top ELT/TECH Org/Bio |
- |
| - |
1990Return to top ELT/TECH Org/Bio |
- |